'Evidence of Hinduphobia': US research finds evidence of sharp rise in hate speech cases against Hindus on social media
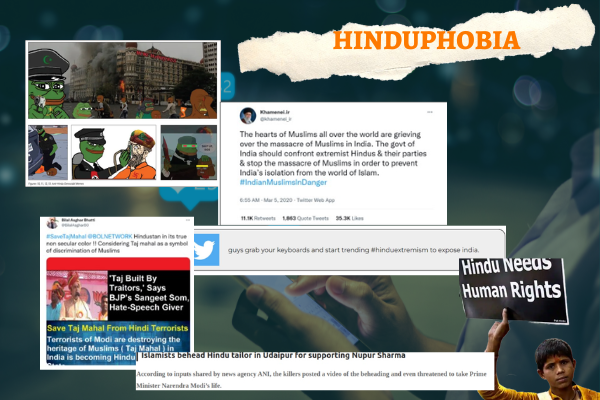
As per the paper titled “Anti-Hindu Disinformation: A Case Study of Hinduphobia on Social Media”, multiple actors, including white supremacists, 4Chan, and other extremists, are widely sharing genocidal Pepe memes against Hindus among Islamist web networks through messaging services such as Telegram and other platforms.
Total Views | 201
New Delhi, July 13: In a shocking development, the researchers at New Jersey's Rutgers University have tracked a rise in Hinduphobia on social media and other messaging platforms. The researchers found "evidence of a sharp rise and evolving patterns of hate speech directed toward the Hindu community across numerous social media platforms."
The investigation revealed that over the past few years, hate speech against the Hindu community has grown mostly unnoticed on social media.
As per the paper titled “Anti-Hindu Disinformation: A Case Study of Hinduphobia on Social Media”, multiple actors, including white supremacists, 4Chan, and other extremists, are widely sharing genocidal Pepe memes against Hindus among Islamist web networks through messaging services such as Telegram and other platforms.
The research revealed that not all anti-Hindu tweets come from Pakistan. Researchers discovered Iran and other nations have state-sponsored information operations. According to their analysis of 1 million tweets, Iranian trolls spread anti-Hindu stereotypes to sow discord as part of an influence campaign to accuse Hindus of committing genocide against minorities in India. Anti-Hindu Disinformation is masked through the use of ethnic pejoratives, slurs, and coded language.
In a report, they said, "State actors within Iran often weaponize this discourse to ignite conflict between India and Pakistan. The weaponization of Hinduphobia for facially political aims in the real world poses a tangible threat to ratchet anti-Hindu violence."
Non-state actors like ISIS-K are also involved in such propaganda. The researchers pointed out how the recent attack on Gurudwara in Kabul was linked by ISIS-K to the alleged derogatory remarks against Prophet Mohammed by former BJP spokesperson Nupur Sharma.
“There is, unfortunately, nothing new to the bigotry and violence faced by the Hindu population,” said John J. Farmer Jr., director of both the Miller Center and the Eagleton Institute of Politics at Rutgers University-New Brunswick. “What is new is the social media context in which hate messages are being shared. Our prior work has shown a correlation between the intensity of hate messaging over social media and the eruption of real-world acts of violence.”
Data collection and analysis were done in collaboration with high school students from the New Jersey Governors' STEM Scholars programme. They instructed them on open-source intelligence gathering, machine learning for detecting cyber-social threats, and the dimensions of anti-Hindu misinformation.
NCRI Anti Hindu Disinformation v2 by Yashwant Poojari on Scribd






